5. BSB-LAN: Query and Control
Because the webinterface basically is just set ‘on top’ to achieve access without further programs like FHEM or openHAB, it’s possible to access the functions and parameters with external programs.
5.1 URL Commands
| Note |
|---|
| The values and parameters in the following list of the URL commands must be written without the brackets. E.g.: URL command /<x> for the simple query of parameter 8700 = /8700. |
| URL Command | Effect |
|---|---|
/<x> |
Query value/setting of parameter <x> |
/<x>!<addr> |
Query value/setting of parameter <x> for destination address <addr> |
/K<x>!<addr> |
Query all parameters of category <x> for destination address <addr> |
/<x>/<y>/<z> |
Query values/settings of parameters <x>, <y> and <z> |
/<x>-<y> |
Query values/settings of parameters <x> to <y> |
/<x>!<addr>-<y> |
Query values/settings of parameters <x> to <y> for destination address <addr> |
/A=0 |
Disable 24h average calculation temporarily Disables the 24h average calculation temporarily (until the next reboot of the microcontroller). For a complete deactivation, uncomment all parameters for that function in the file BSB_LAN_config.h. |
/A=<x>,<y>,<z> |
Change 24h average value calculation of parameters <x>, <y>, <z> During runtime up to 20 new parameters can be defined for the 24h average calculation. These parameters are kept until the next reboot of the microcontroller. |
/B0 |
Reset counter of accumulated burner-runtime and -cycles |
/C |
Configuration page (aka webconfig) of BSB-LAN |
/CO |
Display the configuration of BSB-LAN |
/D or /DD |
Display logfile from the microSD-card Displays the logfile datalog.txt which contains the values of the logged parameters defined in the file BSB_LAN_config.h. |
/D0 |
Reset both logfiles & create new header This command deletes the content of the files datalog.txt and journal.txt and creates a new csv-header for datalog.txt. This command should be executed before first logging. |
/DD0 |
Remove logfile datalog.txt only |
/D<a>,<b> |
Displays the data from the logfile which are between <a>,<b> <a> and <b> have to be set in the format yyyy-mm-dd (e.g. /D2023-04-01,2023-04-30) |
/D<n> |
Displays the newest <n> calender days of the logfile |
/DG |
Graphical display of the logfile from microSD-card Shows graphical output (graphs) of the logged values. Note: If you use Javascript blockers, make sure you allow access to cdn.jsdelivr.net and d3js.org, because the microcontroller just loads the csv-file into the browser and the D3-framework converts the data. Alternatively, these frameworks can also be stored and used locally - notes on this can be found in the *BSB_LAN_config.h.default* file. If the log file is opened via web interface by clicking on "Display log file", the log data of the most recent n calendar days (n=DEFAULT_DAYS_TO_PLOT, configurable in BSB_LAN_config.h) is displayed graphically first by default. Subsequently, controls on the web page can be used to select a different range, depending on the data contained in the log file. Mouseover, click and mouse wheel actions within the graphical display provide various control options: - better legibility for value numbers with plot lines close to each other (mouseover on plot) - user can interactively highlight plot lines for improved overview (mouseover on legend entries) - user can interactively disable plot lines for improved overview and vertical scaling (click on legend entries) - added zoom (mousewheel/pinch on plot) and pan capability (drag zoomed-in plot) |
/DJ |
Display logfile journal.txt from the microSD-card Displays the logfile journal.txt which shows the content of received and transmitted telegrams. This log is useful for debugging and the search for unknown parameters. To use this function, you must enable the LOGGER module in the file BSB_LAN_config.h and set the first element of the log_parameters array to 30000. |
/DJ0 |
Remove logfile journal.txt only |
/DK<n> |
Deletes the data of the logfile except the last <n> calender days |
/E<x> |
Display ENUM-values of parameter <x> At this command the adapter doesn't communicate with the controller, it's a software sided internal function of BSB-LAN. This command is only available for parameters of the type VT_ENUM, VT_CUSTOM_ENUM, VT_BITS and VT_CUSTOM_BITS. |
/G<x> |
GPIO: Query pin <x> Displays the actual state of GPIO pin <x>, where <y>=0 is LOW and <y>=1 is HIGH. |
/G<x>=<y> |
GPIO: Set pin <x> to HIGH (<y> = 1) or LOW (<y> = 0) Sets GPIO pin <x> to LOW (<y>=0) or HIGH (<y>=1). Reserved pins which shouldn't be allowed to be set can be defined previously at GPIO_exclude in the file BSB_lan_config.h. |
/G<x>,I |
GPIO: Query pin <x> while setting to INPUT If e.g. a coupling relay is connected to a GPIO pin and the state should just be queried, this command should be used. It sets the GPIO pin to input (default they are set to output) and keeps this as long until it's changed by using G<x>=<y>. After that, it's set to output again until the next "I" sets it to input again. |
/I<x>=<y> |
Send INF-message to parameter <x> with value <y> Some values can't be set directly, the controller gets these values by a TYPE_INF-message. As an example, the room temperature of 19.5°C should be transmitted: http://<ip-address>/I10000=19.5. |
/JB |
JSON: Backup of all settable parameters of the controller of the heating system (restore with /JS) |
/JC=<x>,<y>,<z> |
JSON: Query possible values for parameters <x>, <y> and <z> for ENUM type parameters The format of the returned data is the same as the command /JK=<x>. Unlike the /JQ command, it does not return the current parameter values. |
/JI |
JSON: Display configuration of BSB-LAN |
/JK=<x> |
JSON: Query all parameters of category <x> |
/JK=ALL |
JSON: List all categories with corresponding parameter numbers |
/JL |
JSON: Creates a list of the configuration in JSON format |
/JQ=<x>,<y>,<z> |
JSON: Query parameters <x>, <y> and <z> |
/JQ |
JSON: Query parameters |
/JR<x> |
JSON: Query reset-value of parameter <x> Within the integrated operational unit of the heating system there are reset options available for some parameters. A reset is done by asking the system for the reset value and setting it afterwards. |
/JS |
JSON: Set parameters |
/JV |
JSON: Queries the version of the JSON-API. Payload: {"api_version": "major.minor"} |
/JW |
JSON: Reads the list of configuration created with /JL and adjusts the settings. |
/K |
List all categories At this command the adapter doesn't communicate with the controller, it's a software sided internal function of BSB-LAN. |
/K<x> |
Query all parameters and values of category <x> At this command the adapter doesn't communicate with the controller, it's a software sided internal function of BSB-LAN. |
/L=0,0 |
Deactivate logging to microSD-card temporarily In general, the activation/deactivation of the logging function should be done in the file BSB_lan_config.h before flashing the microcontroller. During runtime the logging can be temporarily deactivated by using L=0,0 though, but it only has an effect until the next reboot of the microcontroller. |
/L=<x>,<y1>,<y2>,<y3> |
Set logging interval to <x> seconds with (optional) logging parameter <y1>,<y2>,<y3> This command can be used to change the logging interval and the parameters that should be logged during runtime. All parameters that should be logged have to be set. After a reboot of the microcontroller, again only the parameters are logged which has been defined in BSB_lan_config.h initially. |
/LB=<x> |
Configure logging of bus-telegrams: only broadcasts (<x>=1) or all (<x>=0) When logging bus telegrams (log parameter 30000 as the only parameter), only the broadcast messages (<x>=1) or all telegrams (<x>=0) are logged. |
/LD |
Disable logging of telegrams to journal.txt |
/LE |
Enable logging of telegrams to journal.txt |
/LN |
Forces logging irrespective of current interval and restarts the configured interval at this point of time |
/LU=<x> |
Configure logging of bus-telegrams: only unknown (<x>=1) or all (<x>=0) When logging bus telegrams (log parameter 30000 as the only parameter), only unknown command ids (<x>=1) or all telegrams (<x>=0) are logged. |
/M<x> |
Activate (<x> = 1) or deactivate (<x> = 0) bus monitor mode By default bus monitor mode is deactivated (<x>=0). When setting <x> to 1, all bytes on the bus are monitored. Each telegram is displayed in hex format with a timestamp in miliseconds at the serial monitor. The html output isn't affected though. To deactivate the monitor mode, set <x> back to 0: /M0. |
/N |
Reset & reboot microcontroller (takes approx. 15 seconds) Reset and reboot of the microcontroller. Note: Function must be activated in BSB_lan_config.h by #define RESET |
/NE |
Reset & reboot microcontroller (takes approx. 15 seconds) and erase EEPROM Reset and reboot of the microcontroller with additional erasing of the EEPROM. Note: Function must be activated in BSB_lan_config.h by #define RESET |
/P<x> |
Set bus type/protocol (temporarily): <x> = 0 → BSB / 1 → LPB / 2 → PPS Changes between BSB (<x>=0), LPB (<x>=1) and PPS (<x>=2). After a reboot of the microcontroller, the initially defined bus type will be used again. To change the bus type permanently, adjust the setting setBusType config in BSB_lan_config.h accordingly. |
/P<x>,<y>,<z> |
Set bus type/protocol <x>, own address <y>, target address <z> (temporarily) Temporarily change of the set bus type and addresses: <x> = bus type (0 = BSB, 1 = LPB, 2 = PPS), <y> = own address and <z> = destination address Empty values leave the address as it is already set. |
/Q |
Check for unreleased controller-specific parameters |
/R<x> |
Query reset-value of parameter <x> Within the integrated operational unit of the heating system there are reset options available for some parameters. A reset is done by asking the system for the reset value and setting it afterwards. |
/S<x>!<z>=<y> |
Set value <y> for parameter <x> with optional destination address <z> Command for setting values (therefore, write-access must be defined previously in BSB_lan_config.h!). Additionally a destination address can be set by using <z>. If <!z> isn't used, the standard destination address will be used. To set a parameter to 'off/deactivated', just use an empty value: http://<ip-address>/S<x>= |
/U |
Displays the user-defined variables if used in BSB_lan_custom.h For the creation of one’s own subroutines in BSB_lan_config.h two arrays of 20 bytes size, custom_floats[] und custom_longs[], are available. If used, these can be displayed via URL command /U and can be useful to query own sensors in BSB_lan_custom.h and display the results on the web-interface via /U. |
/V<x> |
Activate (<x> = 1) or deactivate (<x> = 0) verbose output mode The preset verbosity level is 1, so the bus is 'observed' and all data are displayed in raw hex format additionally. If the mode should be deactivated, <x> has to be set to 0: /V0 Verbosity mode affects the output of the serial monitor as well as the (optional) logging of bus data to microSD card. Therefore the card could run out of space quickly, so it's advisable to deactivate the verbosity mode already in the BSB_lan_config.h: byte verbose = 0 The html output isn't affected by /V1. |
/W |
With a preceding /W the URL commands C, S and Q return data without HTML header and footer (e.g.: /WC or /WS<x>=<y!z>); module WEBSERVER has to be compiled! |
/X |
Query optional MAX!-thermostats Queries and displays the temperatures of optional MAX!-thermostats. Note: MAX!-components have to be defined in BSB_lan_config.h before! |
5.2 MQTT
BSB-LAN supports the MQTT protocol, so the values and settings of the heating controller can be retrieved via MQTT.
To use MQTT with BSB-LAN, it is mandatory that the definition “#define LOGGER” in the file BSB_LAN_config.h is activated. This is already the case in the default setting.
The parameters to be sent (queried by BSB-LAN, the transmission interval (only one interval possible for all parameters!) and the other MQTT-specific settings (broker, topic, etc.) are to be set either via web configuration or directly in the file BSB_LAN_config.h. Please refer to the explanations in the corresponding subchapters of chap. 5.
Examples for an integration of BSB-LAN can be found in the corresponding subchapters of chap. 11.
| Note |
|---|
| If you use the MQTT function with fixed logging parameters and logging interval, make sure that you adjust the logging interval (= MQTT send interval)! By default 3600 is set here, which means that the parameters are sent every 3600 seconds, so every 60 minutes and thus hourly! So if you set up your MQTT broker and you wonder why you don’t receive values, check the logging interval at first place! |
BSB-LAN uses the subtopic “status” below the defined “MQTTTopicPrefix” to publish its online state. Based on the default setting this would be “BSB-LAN/status”. This allows you to track whether BSB-LAN is actually publishing current readings and able to receive commands.
If BSB-LAN is available, the topic contains the value “online”, otherwise you’ll see “offline”. The message is made persistant via the retain-flag, thus, the subscriber does not have to have the topic subscribed during BSB-LAN startup.
Any restart initiated by the firmware (e.g. the URL-command /N) will immediately set the topic to “offline”. Any uncontrolled shutdown (e.g. a power outage or some firmware flashing) will cause the broker to transmit the offline-message after a (broker specific) timeout.
In addition to (broker-side) pure receiving, it is also possible to query and/or send control commands (URL commands /S and /I) to BSB-LAN from the broker via MQTT. Of course, BSB-LAN must be granted write access to the controller if one wants to change settings.
The command syntax is:
set <MQTT server> publish <topic> <command>
-
<MQTT server>= The name of the MQTT server. -
<topic>= Default setting is “BSB-LAN”, otherwise the defined “MQTTTopicPrefix” in the file BSB_LAN_config.h accordingly. If no topic is defined (not advisable), “FromBroker” must be taken as topic. -
<command>= The query of the specific parameter or the corresponding parameter-specific URL commandSorI.Attention Only one query/command is possible at a time, so no parameter ranges can be queried!
Subsequently BSB-LAN sends back an acknowledgement of receipt (“ACK_<command>”).
| Example |
|---|
The command set mqtt2Server publish BSB-LAN S700=1 sends from the MQTT broker named “mqtt2Server” the command “S700=1” with the topic “BSB-LAN” and causes a mode switch to automatic mode. |
The command set mqtt2Server publish BSB-LAN 700 sends from the MQTT broker named “mqtt2Server” the command “700” with the topic “BSB-LAN” and causes a query of parameter 700. |
| Example for Mosquitto |
|---|
Command for querying parameter 1010 (incl. username & password): mosquitto_pub -h 192.168.178.35 -u USER -P PASSWORD -m "1010" -t BSB-LAN -d |
Command for setting parmeter 1610 to 41° (incl. username & password): mosquitto_pub -h 192.168.178.35 -u USER -P PASSWORD -m "S1610=41" -t BSB-LAN -d |
5.3 JSON
-
Query of categories:
http://<ip-address>/JK=<xx>
Query of a specific category (<xx>= number of category)http://<ip-address>/JK=ALL
Query of all categories (including min. and max.) -
Query and set parameters via HTTP POST:
For this the following URL commands have to be used:
http://<ip-address>/JQto query parameters
http://<ip-address>/JSto set parametersThe following parameters are usable within these URL commands:
http://<ip-address>/JQ Send: "Parameter" Receive: "Parameter", "Value", "Unit", "DataType" (0 = plain value (number), 1 = ENUM (value (8/16 Bit) followed by space followed by text), 2 = bit value (bit value (decimal) followed by bitmask followed by text/chosen option), 3 = weekday, 4 = hour:minute, 5 = date and time, 6 = day and month, 7 = string, 8 = PPS time (day of week, hour:minute)), "readonly" (0 = read/write, 1 = read only parameter), "error" (0 - ok, 7 - parameter not supported, 1-255 - LPB/BSB bus errors, 256 - decoding error, 257 - unknown command, 258 - not found, 259 - no enum str, 260 - unknown type, 261 - query failed), "isswitch" (1 = it VT_ONOFF or VT_YESNO data type (subtype of ENUM), 0 = all other cases) http://<ip-address>/JS Send: "Parameter", "Value", "Type" (0 = INF, 1 = SET) Receive: "Parameter", "Status" (0 = error, 1 = OK, 2 = parameter read-only) -
The query of multiple parameters within one command is also possible:
The commandhttp://<ip-address>/JQ=<x>,<y>,<z>queries the parameters<x>, <y>, <z>. -
Example for setting parameters via Linux command line or „Curl for Windows“ with parameter 700 (operating mode heating circuit 1) → set to 1 (= automatic mode):
Linux command line:
curl -v -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '{"Parameter":"700", "Value":"1", "Type":"1"}' http://<ip-address>/JSCurl for Windows:
curl -v -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d "{\"Parameter\":\"700\", \"Value\":\"1\", \"Type\":\"1\"}" http://<ip-address>/JS
User “hacki11” developed a detailed and interactive documentation of the JSON API.
Thanks a lot!
| Note for developers |
|---|
| The API can be tested on your own system using Postman. To do this you have to add the URL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fredlcore/bsb_lan/master/openapi.yaml in File/Import/Link and (if necessary) change the specific settings like address, basic auth data etc. |
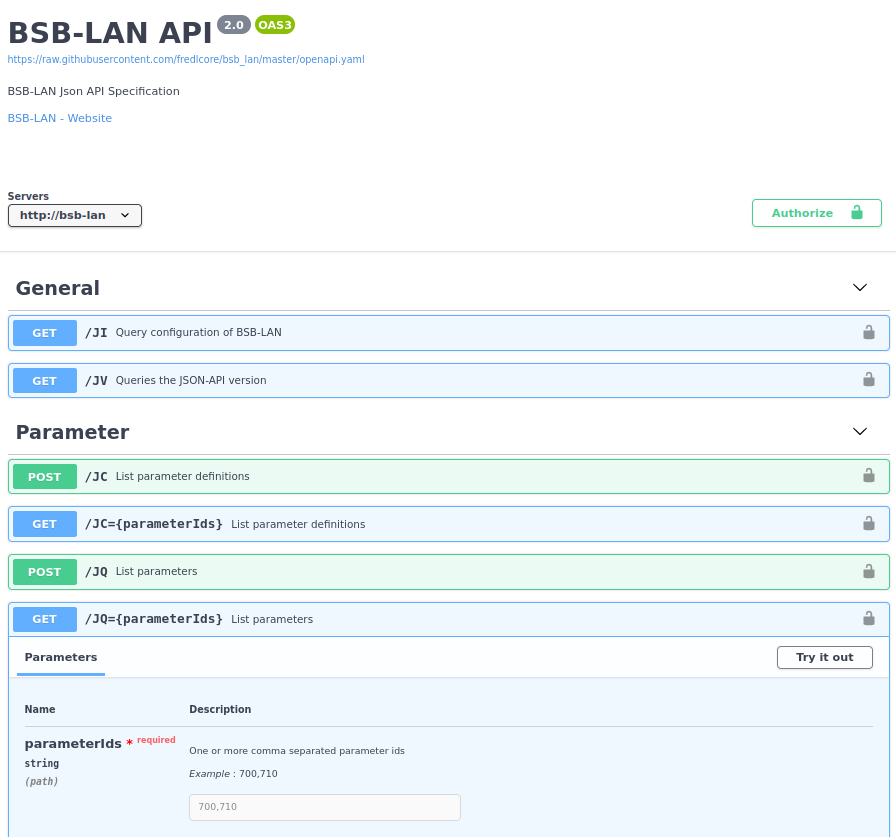
In addition to the descriptions including examples of the individual commands, all informations about the types, formats, possible values, etc. sre also listed.
| Notes |
|---|
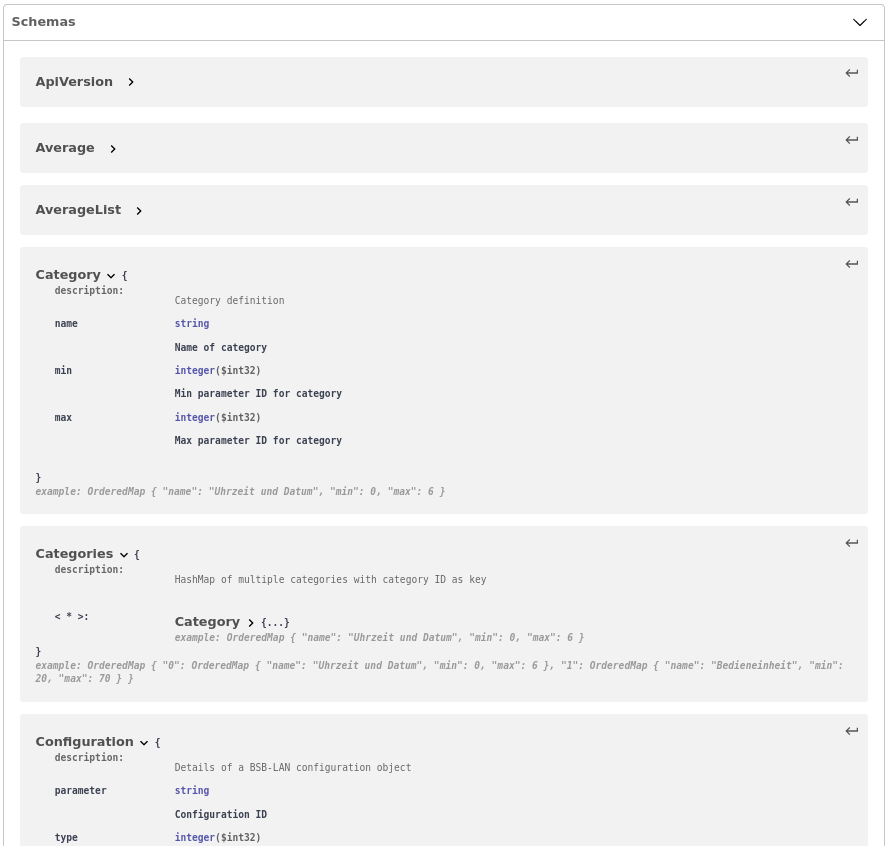
| JSON commands can also be used via Linux command line or “Curl for Windows”. In the above mentioned interactive API documentation, the corresponding Curl commands can be generated and then copied for further use (the IP must be adjusted). To do this, proceed as follows: 1. Click on the desired operation, e.g. “/JQ={parameterIds}”. 2. Click on “Try it out” on the right side of the window. 3. Enter the desired parameter(s) (in the example shown below: 700,8300). 4. Click on “Execute”. In the “Responses” field you will see the URL and Curl commands you can copy. |
Attention: The character combination %2C when listing multiple parameters is inserted by Swagger instead of the comma. If you want to copy and use the URL/Curl commands, please replace each %2C with a , (comma)! |
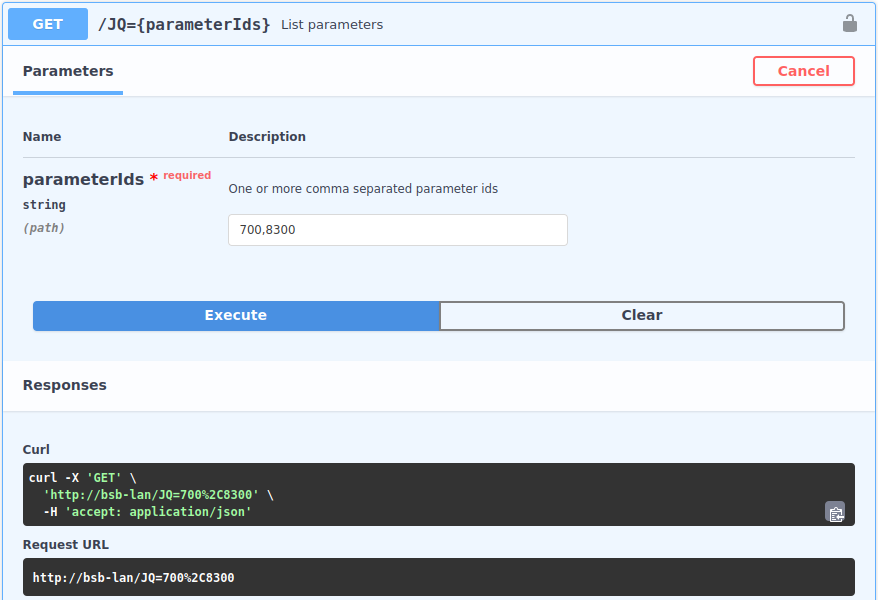
The output of the URL/Curl command.
5.4 Special Parameters & Number Ranges
Since BSB-LAN version 3.x, certain functions had to be implemented as special parameters using parameter numbers 10000 and upwards. The following list shows these parameters including the number and the belonging function. Depending on the type of command, you either have to use a SET or INF command (write access has to be granted), see the mentioned chapters for further informations.
| Parameter Number | Function | Command Type |
|---|---|---|
| 10000 | Room Temperature HC1 | INF - see chap. 6.3 |
| 10001 | Room Temperature HC2 | INF - see chap. 6.3 |
| 10002 | Room Temperature HC3 | INF - see chap. 6.3 |
| 10019 | Manual DHW Push | SET - see chap. 6.5 |
| 10110 | Presence Button HC1 (temporary heating mode change) | SET - see chap. 6.4 |
| 10111 | Presence Button HC2 (temporary heating mode change) | SET - see chap. 6.4 |
| 10112 | Presence Button HC3 (temporary heating mode change) | SET - see chap. 6.4 |
Number Ranges
The following overview shows how the number ranges are divided or assigned.
| Number Range | Usage |
|---|---|
| 0-9999 | Parameters of the controller |
| 10000-10019 | Functions of the room unit (room temperature & DHW push) |
| 10020-10099 | Originally parameters without numbers from the controller |
| 10100-10109 | Broadcast parameters |
| 10110-10129 | Presence button (temporary change of heating mode) |
| 10200-10999 | Range for manually added parameters |
| 20100-20199 | Sensors: DHT22 |
| 20200-20299 | Sensors: BME280 |
| 20300-20499 | Sensors: DS18B20 |
| 20500-20699 | MAX! sensors/components |
